INDEX
(Not linked)
SCROLL DOWN FOR RHYMING STUDY AIDS
Location in Human Anatomy
Direction of Flow
Metabolism
Homeostasis
Organ Cells
Human Organ Systems
Endocrine System
Adrenal Gland
Pancreas
Pineal Gland
Pituitary Gland
Thyroid Gland
Cardiovascular/Respiratory System
Heart Valves
Aortic Arch
Arterial Blood pH
Direction of Flow
Metabolism
Homeostasis
Organ Cells
Human Organ Systems
Endocrine System
Adrenal Gland
Pancreas
Pineal Gland
Pituitary Gland
Thyroid Gland
Cardiovascular/Respiratory System
Heart Valves
Aortic Arch
Arterial Blood pH
Blood Gas Exchange
Blood Oxygen
Lungs and Gas Exchange
Nervous System
Brachial Plexus
Nervous System
Brachial Plexus
Brain Lobes
Embryonic Brain
Cranial Nerves
Digestive System
Digestion of Nutrients
Digestion of Nutrients
Swallowing
Liver
Bile and Fat Metabolism
Liver
Bile and Fat Metabolism
Integumentary System
Dermis
Epidermis
Epithelial Cells
Ear
Eye
Dermis
Epidermis
Epithelial Cells
Ear
Eye
Attributions at the end of this page.
Location in Human Anatomy
Top is cranial or superior
Bottom caudal* or inferior,
Front is ventral** or anterior
Back is dorsal or posterior.
Medial means middle
And the side is lateral,
In from extremities proximal
Moving toward them is distal.
Cranium
*Cerebellum, below and behind
Caudal is location assigned.** The forehead (front) is referred
As rostral, a different word.
By Alan Beech
Direction of Flow
Afferent and efferent respectively mean to or from any center.
To or from the CNS or to or from glomeruli etc.
Afferents approach
But efferents exit.
By Alan Beech
Metabolism
All reactions on a live cell
How it integrates as well
Define the mechanism
We call metabolism.
By Alan Beech
Homeostasis
Holding off change is
Homeostasis.
The hypothalamus embraces
Metabolic homeostasis.
By Alan Beech
Organ cells
Cells parenchymal
In organs are functional.
Each stromal organ cell
Supports the others well.
By Alan Beech
The 11 systems are integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular,
lymphatic, respiratory,digestive, excretory, reproductive.
lymphatic, respiratory,digestive, excretory, reproductive.
Lungs, bones, meat
Steroids, heart, eat,
Sex, fear, excrete,
Skin, bugs defeat.
By Alan Beech
Endocrine
System
Public Domain (US Gov't)
Endocrine glands
make hormone exudations
Secreted
straight into blood circulations.
Pituitary,
pancreas, pineal,
Parathyroid,
thyroid and adrenal.
The hormones
for sex and for stuff that we eat.
Testes,
ovaries and GI tract secrete.
Adrenal Gland
By EEOC
Renal, to the kidney pertains;
Adrenal, on the kidney reigns.
And its outer tissue or cortex
Makes corticoids and androgens (sex).
Medulla of this gland
Is the “fight or flight” land,
Norepi- and epinephrine secreted
And by sympathetic stimulus meted.
By Alan Beech
Pancreas
Public domain
Pancreatic tissue is seen
Twixt duodenum and spleen.
Makes lipase and proteases exocrine
And insulin and glucagon endocrine.
Islet of Langerhans hormone factories
Connect directly to blood capillaries.
Its digestive enzymes into acini flow
Via pancreatic duct to duodenum go.
By Alan Beech
Pineal
Gland
Located twixt left and right thalamus see
The pineal gland,
like a pine cone or pea.
Secretes
melatonin, body rhythm hormone
Controls the sleep
pattern, full function not known.
Pituitary Gland
By Patrick J. Lynch
By Life Sciences Database
The pea-sized pituitary gland
Is the endocrine central command
Anterior part comes from oral ectoderm
Posterior part comes from neuro-ectoderm.
The posterior lobe has less stuff made in
Just oxytocin and vasopressin.
O constricts the uterus, promoting lactation
V raises blood pressure and water retention.
Anterior lobe, endocrine throne
Place where controlling hormones are grown.
Makes corticoid controller ACTH
Sex hormones prolactin, LH, FSH.
Other anterior lobe hormones grown
Include somatotropin (growth hormone).
The thyroid hormone controller thyrotropin
An endorphin and (satiety) leptin.
By Alan Beech
Thyroid
Gland
By CFCF
Under the Adam’s
Apple, like a bow tie
Around the
trachea, the thyroid lobes lie.
Thyroxin (T4)
is their main hormone
Also T3 and some
others are known.
Promoting
growth of every body cell
And boosting
all metabolism as well.
Cardiovascular
system
Left ventricle, aorta, artery,
arteriole,
Capillary, venule, vein and right auricle.
On to the lungs, fresh oxygen to gain
Back to the heart to be pumped round
again.
Heart Valves
By GFDL
Two pumps in sync in one heart,
Left and right hearts never part.
Tired blood to right atrium flows
Then through tricuspid valve it goes.
After tricuspid the right ventricle
Ejects the blood to lungs when full
Pulmonary valve prevents backflow
To alveolar capillaries it must go.
More HbO2 the blood now gains
Back to heart by pulmonary veins.
To the left atrium the blood will cycle
Through mitral valve to left ventricle.
The aortic valve at start of aorta
Stops back flow that didn’t oughta.
The mighty left ventricle muscle
Pumps the whole systemic cycle.
By Alan Beech
Aortic
Arch
The
super highway blood transporter
At
high pressure is the aorta.
At
aorta root two junctions we see
Left
and right coronary artery.
At
top of the arch three branches spread
Supplying
blood to the arms and head,
First
brachiocephalic artery that soon splits
To
subclavian and common carotid (right) bits.
Left
common carotid is second branch of three
Third
branch is the left subclavian artery.
Arch
chemo- and baroreceptors inform
The
brain how its blood parameters perform.
By Alan Beech
Arterial Blood pH
Civilized man before
7.35
AM is not lucid.
Arterial blood below
7.35
pH is too acid.
By Alan Beech
Blood
Gas Exchange
Beds of capillaries
RBCs tightly squeeze.
Oxygen squeezed out too
Replaced by CO2.
CO2 also faces
Carbonic anhydrases
The ion they create
Is bicarbonate.
Alveolar capillaries
Also squeeze RBCs
So they lose CO2
Then add oxygen new.
By Alan
Beech
Renal detective cells know
When blood oxygen is low,
Ethyropoietin
They begin secretin’.
Into blood it will go
To tell bone marrow
To output please
More RBCs.
By Alan Beech
Public domain
Lungs, called lights in butchery
Float on water if set free.
Alveoli exchange gases
With each breath a person passes.
The RBCs on their way through
Lose CO2 and add O2.
Hemoglobin plus O2
Makes RBCs look red and new,
Until they reach capillaries
And must endure another squeeze.
Compressed, they release oxygen
Set free, gain CO2 again.
By Alan Beech
Nervous System
By Fuzzform
The initial division pair
Central and peripheral share.
Royally does central reign
Over spinal cord and brain.
Afferent (sensory) provides
Intelligence, the brain decides
Effective action essentials
By efferent (motor) potentials.
Peripheral NS divide,
Somatic NS one side
Muscles we call voluntary
CNS directs their itinerary.
Nervous system autonomic
“Fight or flight” sympathetic
Stress hormone releases
And blood pressure increases.
The Parasympathetic
Controls all things pacific.
Saliva, sex and calm rest.
Food, more sex and digest.
By Alan Beech
By Mattopaedia
Ventral rami spinal nerves run
Cervical five to eight and T one
The 5 roots into 3 trunks huddle
C 7 medial (alone in the middle),
C5 and 6 become superior,
C8, T1 become inferior.
Each trunk splits to two divisions
Anterior, posterior named revisions.
The 6 divisions to 3 cords converge,
Posterior cord at posteriors merge.
The lateral cord is born from fusions
Of C5, 6 and 7 anterior divisions.
Anterior divisions of T1 and C8
Combine and cord medial mediate.
The brachial plexus lateral end
Five plus branches distal send.
Enervates whole limb except in
Trapezium muscle, axilla skin.
Names of these five branches are
Axillary, median, ulnar
Musculocutaneous
And radial, not radius.
By Alan Beech
By Washington Irving
Cerebellum, cerebral hemispheres.
And each cerebral hemisphere
Anatomists to four lobes shear.
Frontals front the hemisphere,
Occipitals occupy the rear,
Temporals neighbors to each ear,
Parietals top center near.
Occipital lobes control our eyes.
Parietal sense and place supplies.
Frontals decisions, ethics, history.
Temporals language, ears, memory.
Cerebellum at back down low
Controls movement and how we go.
Brain stem controls respiration,
Consciousness and circulation.
By Alan
Beech
By Nrets
In embryos four brain
parts primal
Are forebrain, mid-,
hind- and cord spinal.
In mature brain the
cord and midbrain remain
The top of the
brainstem is called the midbrain.
Farther down
brainstem other parts are
Pons and medulla
oblongata.
P and m o and
cerebellum
From embryonic
hindbrain come.
Five vesicle stage
forebrain splits in twain
To the diencephalon
and endbrain.
Diencephalon becomes
thalamus plus
Pretectum, hypo-,
sub-, epi-thalamus.
C hemispheres from endbrain
do grow
Also the basal
ganglia below.
Corpus callosum axons
supply
Coupling to
hemispheres they tie.
Deep in the forebrain
thalamus relays
Neurons to cortex in
different ways.
Below thalamus
hypothalamus is
Neural controller of
homeostasis.
By Alan Beech
By Lemen
(One) smells first,
olfactory.
(Two) optic for stuff
we see.
(Three) oculomotor
tie
(Four) with trochlear
round the eye.
(Five) trigeminal the great.
(Six) abducens eyes
rotate.
(Seven) facial faces
near.
(Eight)
vestibulocochlear.
(Nine) the glossopharyngeal.
(Ten) vagus. lungs,
guts, heart and all.
(Eleven) accessory
shoulders can reach.
(Twelve) hypoglossal
tongue, pharynx and speech.
By
Alan Beech
Digestive system
Upper GI tract mouth to duodenum
Lower GI tract anus to jejunum.
Digestion of Nutrients
By Mariana
Ruiz Villarreal
"We are what we
eat"
Digestive enzymes
Break down our meat
The belly helps as
well
Secreting HCl.
"We are what we
eat"
Belly makes chyme, to
Digest, absorb,
excrete.
Proteins and starch
decompose,
To amino acids and
glucose.
“We are what we eat”
Satiating foods
Help us to feel
replete.
Foods with sugar and
fat
Are not much good at
that.
By Alan Beech
Swallowing
By OpenStax College
The first swallowing stage (or
deglutition)
“Oral” is a voluntary decision.
Chewing makes the saliva flow
Moist bolus to back of tongue go.
Involuntary stage involves the pharynx
The soft palate closes the nasopharynx
The epiglottis closes the trachea
So the path of the bolus is now clear.
Involuntarily the bolus
Is carried down the esophagus.
Peristalsis helps it flow
To the stomach it will go.
By Alan Beech
Liver
By BruceBlaus
Largest internal organ the liver,
Many important tasks can deliver.
Each molecule of food digested
By hepatic cells is first tested.
Toxics it can detoxify,
Many functions we classify,
Glucose to glycogen it regulates,
Proteins and amino acids creates.
Ammonium to urea converted,
Bile synthesized and to duct diverted.
Fatty acids freshly made
To the bloodstream are conveyed.
By Alan Beech
The liver makes bile, it is also called
gall
It helps fats across the intestinal
wall.
Each cholic salt as detergent excels
Breaking up fat into tiny micelles.
Micelles of fat the lipases attack.
As tiny drops have more surface to
crack
To make fatty acids and monoglycerides.
Less lipophilic than (fat) triglycerides.
These less fatty molecules
Cross the enterocyte walls.
In enterocytes many things go on
Fat leaves in lymph as a chylomicron.
Fat chylomicrons and phospholipid are seen
Plus cholesterol esters and
lipoprotein.
Tiny fat spheres make the milky
chyle
In lymph to bloodstream in a short
while.
From liver to duodenum bile flows
From portal vein back to liver it goes.
Except the small fraction that is lost to
feces
Enterohepatic cycling never ceases.
By
Alan Beech
Integumentary
System
The body image
we present
Comprises our
integument.
Cover of skin
and nails and hair
System that
we see when bare.
By Alan Beech
Dermis
Public domain
Dermis, thick inner layer of skin
Fast to the basement membrane is bound.
Joined to the epidermal layer thin
This connective tissue layer is found.
Sebum and sweat glands in dermis exist,
Hair follicles are also found there.
Hair roots and blood vessels on the list
Receptors of nerves both layers share.
By Alan Beech
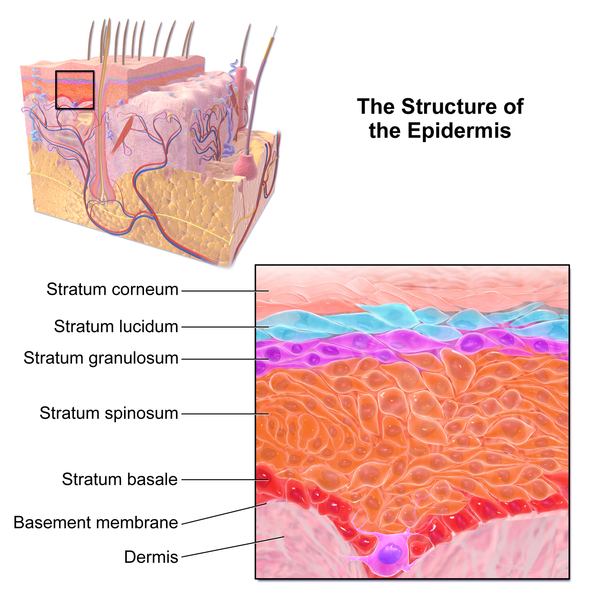
Epidermis
By BruceBlaus
The outermost layer of
human skin,
Epidermis (from ectoderm)
is thin.
Point one millimeter most
places
Point six on palm and sole
faces.
Though epidermis is thin it
Has four plus cell layers in
it.
Five in the palm or foot
sole
Through which cells must
scroll.
Stem cells in the basal
layer divide
And new keratinocytes
provide,
Excess cells squeezed out
alas
And to the layer spinous
pass.
Mitosis and new cells
arriving
Movement out of cells is
driving.
As through layers they
navigate
Cells change and
differentiate.
Tall columnar cells first
fatten
Into cuboid then squamous
flatten.
In the granular layer cells
all die
Cornified shells at the surface lie.
Integument cells we see are
dead
Cornified before they are
shed.
New cells come to take
their place
From the basal layer
interface.
This protector stout
Although it is thin
Keeps the outside out
And the inside in.
By Alan Beech
Epithelial
Cells
Public Domain
Nearly all epidermal
cells
Are also epithelial cells.
This type of cell
lines body surfaces
Arteries, glands and
cavity places.
One layer simple
epithelium
Two or more layers,
stratified become.
Squamous cells
(squashed) at the surface place
Columnar cells
basement membrane face.
By
Alan Beech
The external ear, the pinna we see
Ear
By Dan Pickard
The external ear, the pinna we see
Aims sound at the canal auditory.
Where eardrum or tympanic membrane
Transmit the sound on as vibes again.
Three little ossicles next we see
Malleus, incus, stapes agree
To magnify the vibes you hear
Tiny bones in the middle ear.
The stapes or stirrup is known
To be the body’s smallest bone,
It transmits vibes to the oval window
Then to inner ear liquid they go.
The oval window has a round mate
That lets the liquid inside vibrate.
(Liquids are incompressible alone
And the inner ear is encased in bone.)
The hearing part of the inner ear
Is the hollowed out spiral shaped cochlear
Where vibes in the Organ of Corti send
Sound info to each auditory nerve end.
Also part of the inner ear
Controls the way we balance here.
Saccule and utricle, two locales
And the semicircular canals.
By Alan Beech
Eye
By Holly
Fischer
The eyeball or globe would be a sphere
But for the bump in front, the cornea.
Inside the cornea, the iris and lens
place
To focus light on the retina surface.
Eye has three coats, outermost sclera
Middle the choroid, innermost retina.
Inside the sclera the choroid vascular
Nutrifys optic nerve and macula.
Vitreous humor of sclera ball
Hardly ever changes at all.
Inside the cornea aqueous humor
Flows chambers, post- to ant-erior.
Flowing from ciliary epithelium
The aqueous humor does come
Via the trabecular network corral
Back to blood via Shlemm’s Canal.
Lens held by suspensory ligaments
Ciliary muscles control movements.
The iris aperture controls the right
Amount of light for good
eyesight.
By Alan Beech
Attributions
All rhymes composed by Alan Beech
IMAGE
ATTRIBUTIONS
Human Body Systems
[CC BY 3.0
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
ENDOCRINE
SYSTEM
Endocrine System (Public Domain)
Adrenal Gland (Public Domain)
Pancreas (Public Domain)
From Grey’s Anatomy. Henry Vandyke Carter, via Wikimedia
Commons
Pituitary Gland
By Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator (Image:Skull and
brain sagittal.svg) [GFDL
(http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) or CC
BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)],
via Wikimedia Commons
Thyroid Gland
via Wikimedia Commons
CARDIOVASCULAR
SYSTEM
Heart
See page for author [GFDL
(http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) or CC-BY-SA-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)],
via Wikimedia Commons
Lungs and Gas Exchange (Public Domain)
NERVOUS
SYSTEM
Nervous System Divisions
By The original uploader was Fuzzform at English
Wikipedia [GFDL
(www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html)], via Wikimedia Commons
Brachial Plexus (Public Domain)
By Brachial_plexus.jpg:Mattopaedia at en.wikipedia
derivative work:
Captain-n00dle (talk), MissMJ (Brachial_plexus.jpg), from
Wikimedia Commons
Brain Lobes (Public Domain)
By Original concept by w:User:Washington irving. Current
shape by w:User:Mateuszica.
Color modified by w:User:Hdante. Text labels by
w:User:SAE1962.
SVG by User:King of Hearts. (PNG on English Wikipedia),
via Wikimedia Commons
Embryonic Brain
I, Nrets [GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html),
CC-BY-SA-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)
or CC BY-SA 2.5-2.0-1.0
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5-2.0-1.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
Cranial Nerves
By Brain_human_normal_inferior_view_with_labels_en.svg:
*Brain_human_normal_inferior_view.svg:
Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator derivative work:
Beao derivative work: Dwstultz [CC BY 2.5 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5)],
via Wikimedia Commons
DIGESTIVE
SYSTEM
Digestive System (Public Domain) (NEW)
By Mariana Ruiz Villarreal(LadyofHats) (Own work), via
Wikimedia Commons
Swallowing
Liver
Liver
By BruceBlaus. When using this image in external sources
it can be cited as: Blausen.com staff.
"Blausen
gallery 2014". Wikiversity Journal of Medicine. DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010.
ISSN 20018762.
(Own work) [CC BY 3.0
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
Liver and Gall Bladder (NEW)
or GFDL
(http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html)], via Wikimedia Commons
INTEGUMENTARY
SYSTEM
Dermis (NEW)
By BruceBlaus. When using this image in external sources
it can be cited as: Blausen.com staff.
"Blausen gallery 2014". Wikiversity Journal of
Medicine. DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 20018762.
(Own work) [CC BY 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)],
via Wikimedia Commons
Epidermis
By BruceBlaus. When using this image in external sources
it can be cited as: Blausen.com staff.
"Blausen
gallery 2014". Wikiversity Journal of Medicine. DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010.
ISSN 20018762.
(Own work) [CC BY 3.0
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
Epithelial Cells (Public Domain)
Ear (Public Domain)
By Dan Pickard, via Wikimedia Commons
Eye
By Artwork by Holly Fischer [CC BY 3.0
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons























.jpg)


No comments:
Post a Comment